The Problem – The System Wasn't Built for Us
The current financial infrastructure in emerging markets, particularly Africa, was designed for a different era and different users. It fails to serve the needs of the mobile-first generation and the unique financial behaviors of African communities.

Mobile Money Fragmentation
Current State
- Fragmented systems across different countries and providers
- Complex cross-border transfers with high fees and delays
- Limited interoperability between different mobile money platforms
- No unified experience for users across regions
Impact
- Users struggle with multiple wallets and accounts
- High costs for cross-border transactions
- Limited access to global financial services
- Reduced financial mobility
Outdated Banking Infrastructure
Systemic Issues
- Slow processes - transactions take days or weeks
- High fees - disproportionate costs for small transactions
- Growing distrust among youth who prefer digital solutions
- Limited accessibility in rural and underserved areas
User Experience Problems
- Complex onboarding processes
- Poor mobile experience - designed for desktop banking
- Limited hours and physical branch requirements
- Language barriers and cultural misalignment
Inefficient Community Lending
Chama Limitations
Community savings groups (Chamas) are powerful but still rely on:
- Inefficient manual systems for record-keeping
- WhatsApp and notebooks for communication and tracking
- No automation for payments and distributions
- Limited transparency in fund management
- No yield generation on pooled assets
Missed Opportunities
- $3.4B+ in assets managed inefficiently
- 300K+ groups operating without digital tools
- No credit scoring or risk assessment
- Limited scalability of community finance
Fiat On/Off Ramp Challenges
Crypto Integration Problems
- Limited fiat on/off-ramps for crypto users
- Volatile P2P exchanges with high risk
- Regulatory uncertainty around crypto-fiat conversion
- High fees for currency conversion
- Limited liquidity in local markets
User Barriers
- Complex processes for buying/selling crypto
- Trust issues with unregulated exchanges
- Limited payment methods accepted
- High minimum transaction amounts
Community Platform Gap
Missing Infrastructure
Africa lacks a platform that:
- Truly understands local infrastructure gaps
- Enables community-driven crypto lending
- Supports local launches and token projects
- Integrates with existing financial behaviors
- Respects cultural and social dynamics
Current Alternatives
- Global platforms that don't understand local needs
- Silicon Valley solutions designed for different markets
- Fragmented tools that don't work together
- High barriers to entry for local developers
Grey Markets and Informal Systems
Locked Capital
Billions remain locked in informal systems and grey markets:
- Unbanked populations with significant savings
- Informal lending networks with no digital tools
- Cash-based economies with limited digital integration
- Undocumented transactions with no credit history
Economic Impact
- Reduced financial inclusion for millions
- Limited credit access for small businesses
- Inefficient capital allocation in the economy
- Missed opportunities for wealth creation
The Human Cost
Individual Impact
- Financial exclusion for mobile-first users
- Limited access to credit and financial services
- High costs for basic financial transactions
- Reduced economic mobility and opportunities
Community Growth Challenges
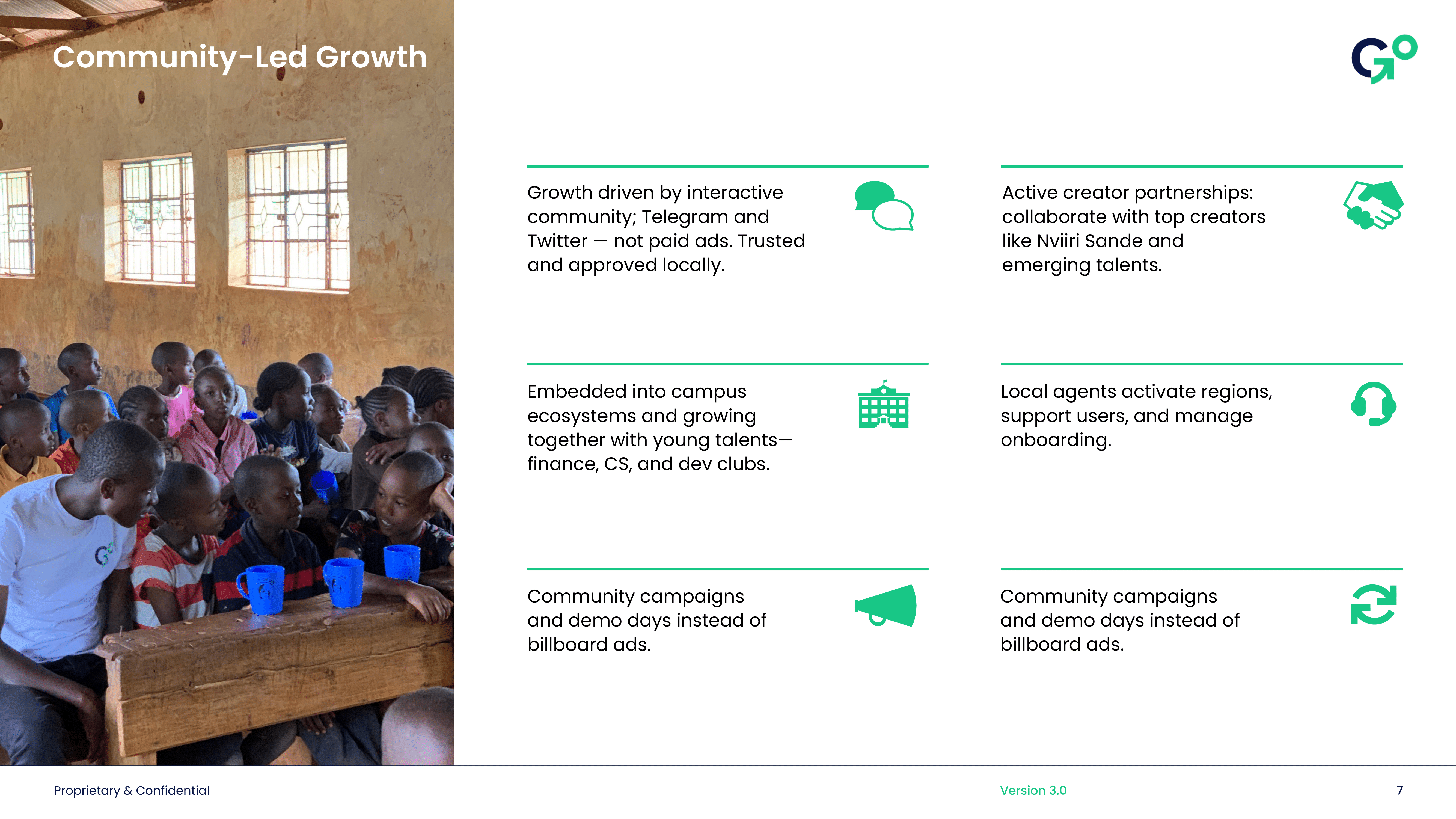

The current state of community finance in emerging markets faces significant barriers that limit growth and development:
- Inefficient community finance systems with manual processes
- Limited scalability of local financial networks
- Fragmented communication through basic tools like WhatsApp
- Manual record-keeping leading to errors and disputes
- No yield generation on community assets
Impact on Communities
The current financial system's limitations have created significant challenges for community development:
- Reduced economic mobility and opportunities
- Limited access to scalable financial tools
- Fragmented systems that don't work together
- Manual processes that are error-prone and slow
- No integration between traditional and digital finance
Economic Impact
- Reduced productivity due to inefficient systems
- Limited innovation in financial services
- Reduced foreign investment due to payment barriers
- Slower economic growth in emerging markets
Why Traditional Solutions Fail
Designed for Different Users
- Desktop-first design in a mobile world
- Individual-focused in a community-driven culture
- Western-centric in African contexts
- Bank-centric in a mobile money world
Lack of Local Understanding
- No cultural sensitivity to local financial behaviors
- Limited language support for local languages
- Poor integration with existing systems
- High barriers to adoption and usage
The Opportunity Cost
What We're Missing
- Billions in dormant capital in informal systems
- Massive market opportunity in underserved populations
- Innovation potential in community-driven finance
- Economic growth through better financial inclusion
The Stakes
- 3+ billion people in emerging markets need better financial tools
- $100B+ in remittances flowing through inefficient systems
- Millions of communities waiting for digital financial tools
- Trillions in economic potential locked in informal systems
This is why GoChapaa exists—to build the financial system that was designed for us, by us, and serves our unique needs in emerging markets.